- By : BCI
- General
- Comments: 0
CAR T-Cell Therapy: Know About It
CAR T-cell therapy is a groundbreaking advancement in cancer treatment, offering hope to patients with certain types of blood cancers. If you or a loved one is considering this treatment, it’s essential to understand what to expect before, during, and after therapy. This guide from our blood cancer specialists in Surat at BCI- Blood and Cancer Institute, helps you understand the process and potential side effects so you can feel informed and prepared.
What Is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor) T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that modifies a patient’s own T cells — key players in the immune system — to recognize and attack cancer cells. This personalized approach has shown remarkable success for leukaemia treatment in Surat, for specific blood cancers like leukaemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
Who Is Eligible for CAR T-Cell Therapy?
Not everyone qualifies for CAR T-cell therapy. It is primarily utilized by blood cancer hospitals in Surat for patients with:
● Relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL)
● Certain types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
● Multiple myeloma
● Other blood cancers when standard treatments have failed.
The cancer specialist in Surat will assess your eligibility based on your overall health, prior treatments, and disease status.
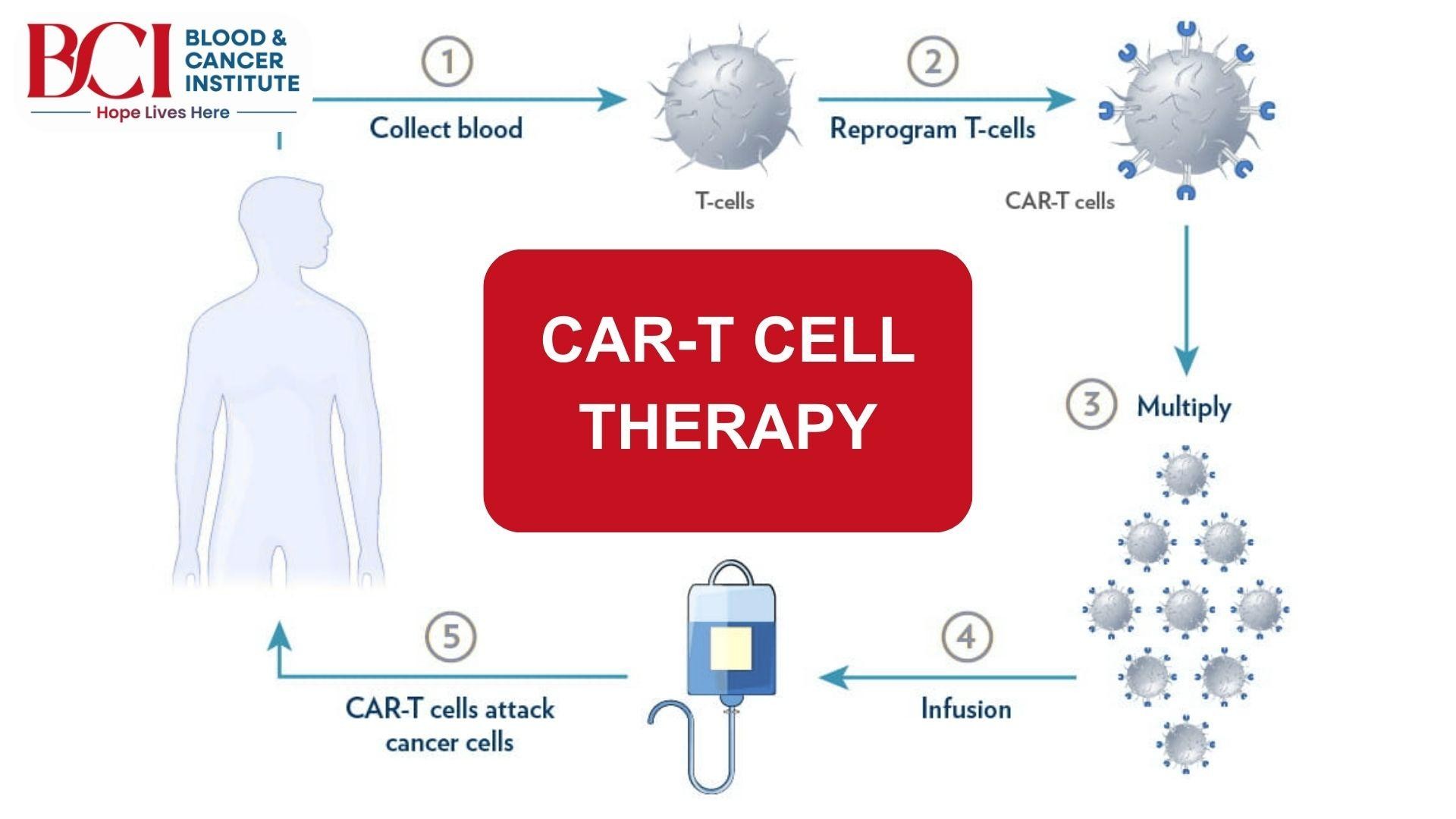
The CAR T-Cell Therapy Process
This treatment involves multiple steps, spanning several weeks to months. Here’s what to expect:
1. T-Cell Collection (Leukapheresis)
The process starts with collecting the patient’s T cells through leukapheresis, a procedure similar to donating blood. Blood is drawn, T cells are separated and collected, and the remaining blood is returned to the body. This step usually takes a few hours.
2. T-Cell Modification in the Lab
The extracted T cells are sent to a specialized lab, where scientists modify them to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). This receptor allows the T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
3. T-Cell Expansion and Preparation
The engineered CAR T-cells are multiplied in the lab until there are millions of them. This process takes about two to three weeks. Meanwhile, patients may undergo chemotherapy (lymphodepleting therapy) to suppress their immune system and make room for the modified T cells to function effectively.
4. Infusion of CAR T-Cells
Once the modified T cells are ready, they are re-infused into the patient through an IV. This is a one-time treatment that takes about 30–60 minutes. Unlike chemotherapy, which is administered in multiple cycles, CAR T-cell therapy is usually a single infusion.
What to Expect After Treatment
Hemato-oncologists in Surat say that CAR T-cell therapy triggers a strong immune response, which can lead to side effects. The most common include:
1. Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
CRS occurs when the activated T cells release a surge of immune system chemicals (cytokines). Symptoms range from mild flu-like effects to severe inflammation. Common signs include:
● High fever
● Low blood pressure
● Difficulty breathing
● Fatigue
CRS usually appears within days after infusion and can last for a week or more. Doctors manage it with supportive care and medications like tocilizumab.
2. Neurological Side Effects
Some patients experience neurological symptoms, known as immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). These can include:
● Confusion or difficulty speaking
● Headaches
● Seizures (in rare cases)
These symptoms usually resolve with time, but medical supervision is crucial.
3. Increased Infection Risk
Since CAR T-cell therapy temporarily weakens the immune system, the risk of infections is higher. Doctors often prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medications as a precaution.
4. Long-Term Monitoring
After treatment, regular follow-ups are essential to monitor for cancer recurrence and manage any lingering side effects. Blood tests and imaging scans help assess how well the therapy is working.
Life After CAR T-Cell Therapy
Many patients experience remission after CAR T-cell therapy, but long-term effects vary. Some key points to keep in mind:
● Success rates vary depending on cancer type and individual factors.
● Fatigue and immune system recovery can take months.
● Secondary cancers or prolonged side effects are rare but possible, requiring continuous medical follow-ups.
Is CAR T-Cell Therapy Right for You?
While this treatment offers promising outcomes, it’s not for everyone. Discuss the benefits and risks with your oncologist to determine if CAR T-cell therapy is the right choice for your condition.
Final Thoughts
CAR T-cell therapy is revolutionizing cancer treatment, offering new hope for patients with difficult-to-treat blood cancers. Understanding what to expect can help you or your loved one navigate the journey with confidence. If you’re considering this therapy, work closely with your medical team at the nearest blood cancer hospital in Surat to ensure the best possible outcome.
