- By : BCI
- General
- Comments: 0
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer vs. Small Cell Lung Cancer: Types, Stages, Symptoms, and Treatment
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. It is broadly categorized into two main types: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). While both originate in the lungs, they differ significantly in their growth patterns, spread, treatment options, and prognosis. Let’s understand the differences from our lung cancer specialists in Surat at BCI- Blood and Cancer Institute, for early detection, effective treatment, and improved patient outcomes.
Understanding the Two Main Types of Lung Cancer
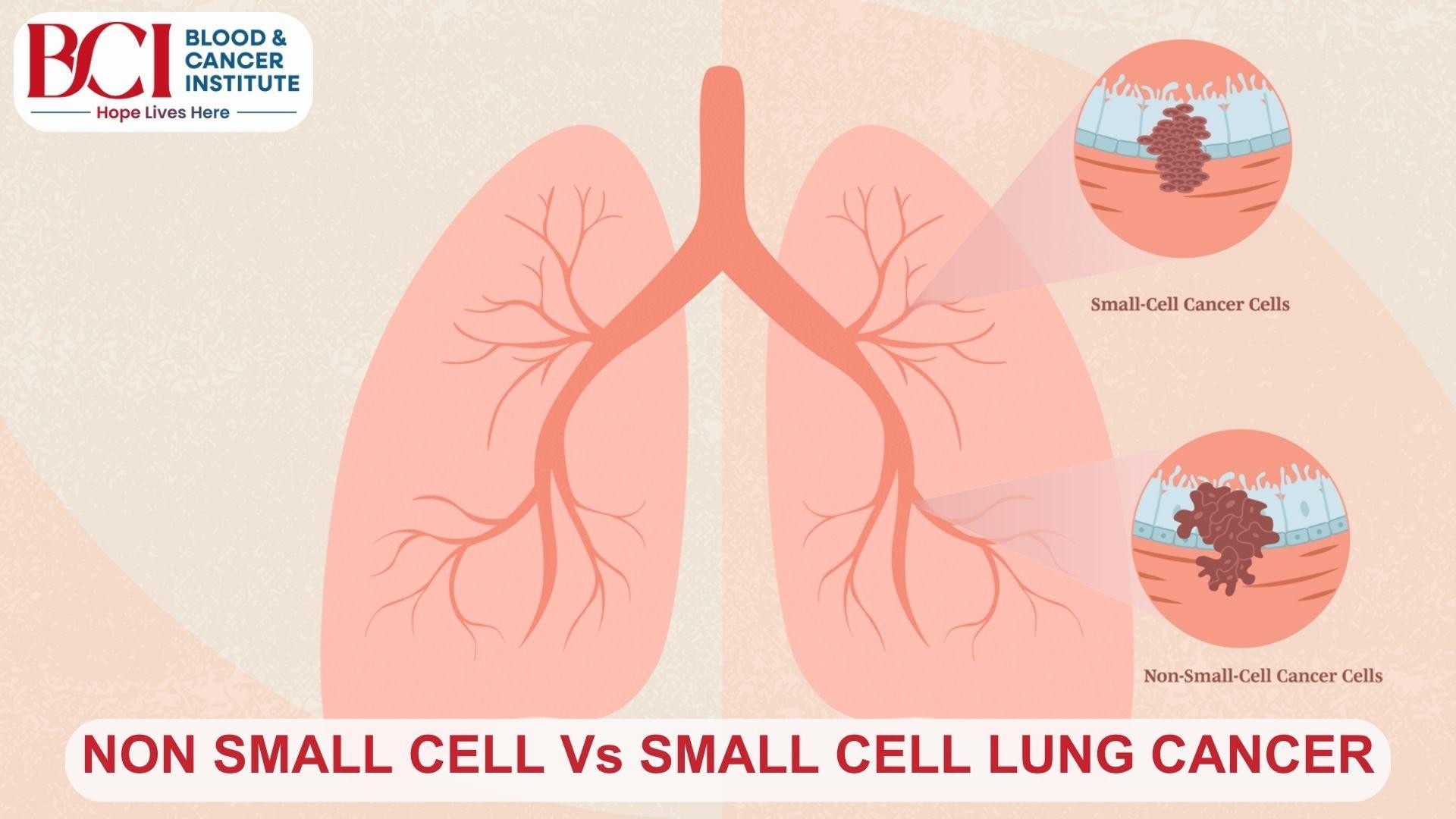
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancer cases, making it the most common type. It typically grows and spreads more slowly than SCLC. The main subtypes of NSCLC include:
- Adenocarcinoma — The most common type, often found in the outer regions of the lungs, primarily affecting non-smokers and former smokers.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma — Usually associated with smoking, it develops in the central part of the lungs near the bronchial tubes.
- Large Cell Carcinoma — A less common, fast-growing form that can appear in any part of the lung.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is far less common, making up about 15% of lung cancer cases, but it is more aggressive. It tends to grow rapidly and spread early to other organs. SCLC is strongly linked to smoking and is typically diagnosed at a more advanced stage due to its rapid progression.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer staging helps determine treatment options and prognosis. The staging differs for NSCLC and SCLC due to their unique growth patterns, says our cancer specialist in Surat.
Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC is staged from Stage 0 to Stage IV, based on the size of the tumor and its spread:
● Stage 0 (In Situ) — Cancer is confined to the lung lining and has not spread.
● Stage I — A small tumor is present but has not spread to lymph nodes.
● Stage II — The tumor has grown larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
● Stage III — Cancer has spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or chest structures.
● Stage IV — The most advanced stage, where cancer has metastasized to other organs like the liver, bones, or brain.
Stages of Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
Cancer specialists in Surat explain that SCLC is classified into two stages:
● Limited Stage — Cancer is confined to one lung and may have reached nearby lymph nodes.
● Extensive Stage — Cancer has spread beyond the lung to other body parts.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer symptoms often go unnoticed in the early stages, leading to late-stage diagnoses. Common symptoms include:
● Persistent cough that worsens over time
● Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
● Shortness of breath and wheezing
● Unexplained weight loss
● Chest pain or discomfort
● Fatigue and weakness
● Hoarseness
● Frequent lung infections (bronchitis or pneumonia)
Since SCLC progresses rapidly, symptoms can appear more suddenly compared to NSCLC.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
Cancer treatment in Surat varies based on cancer type, stage, and overall patient health.
Treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Surgery — Effective in early-stage NSCLC (Stage I or II) where the tumor can be removed.
- Radiation Therapy — Used when surgery is not an option or to shrink tumors before surgery.
- Chemotherapy — Commonly used for later-stage NSCLC or in combination with surgery/radiation.
- Targeted Therapy — Works against specific genetic mutations like EGFR or ALK.
- Immunotherapy — Boosts the immune system to fight cancer cells, often used in advanced cases.
Treatment for Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
Due to its aggressive nature, SCLC requires immediate and aggressive treatment:
- Chemotherapy — The primary treatment, often combined with radiation.
- Radiation Therapy — Used to shrink tumors or prevent cancer from spreading to the brain.
- Immunotherapy — Emerging as a new option for treating advanced SCLC.
Since SCLC spreads early, surgery is rarely an option unless detected extremely early, which is uncommon.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Major Risk Factors
● Smoking — The leading cause of both NSCLC and SCLC.
● Secondhand smoke exposure
● Exposure to radon gas, asbestos, or other carcinogens
● Family history of lung cancer
● Air pollution and occupational hazards
Prevention Strategies
● Quit Smoking — The most effective way to reduce lung cancer risk.
● Avoid Exposure to Carcinogens — Limit exposure to radon, asbestos, and industrial pollutants.
● Regular Screenings — Low-dose CT scans are recommended for high-risk individuals, such as long-term smokers.
● Healthy Lifestyle — A balanced diet and regular exercise can boost overall lung health.
Conclusion
Both NSCLC and SCLC pose serious health risks, but they differ in progression, treatment, and prognosis. Early detection is key — the sooner lung cancer is diagnosed, the better the chances of successful treatment. If you are at high risk or experience persistent symptoms, consult a doctor at Blood and Cancer Institute, one of the best cancer hospitals in Surat, for screening and preventive measures. Awareness and proactive healthcare can save lives.
