- By : BCI
- Blog
- Comments: 0
Understanding Lymphoma: A Complete Guide From The Blood Cancer Specialist in Surat
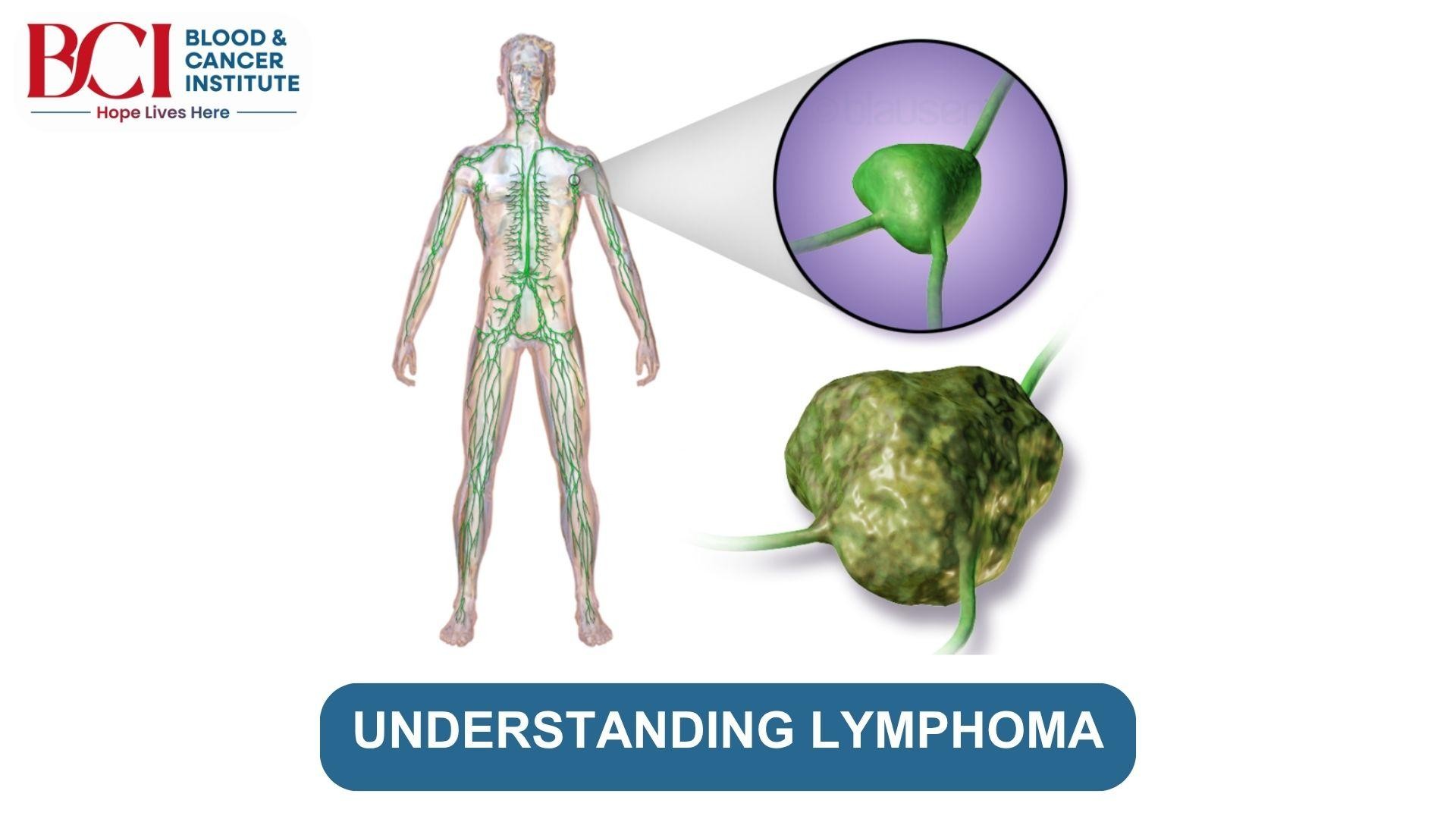
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that begins in the lymphatic system, an essential part of the body’s immune defenses. It occurs when lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, grow uncontrollably and accumulate in lymph nodes and other tissues. Understanding lymphoma is important because early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Although it may sound intimidating, increased awareness and advancements in medical care have made it a manageable condition for many patients. Let’s understand this cancer from our blood cancer specialists in Surat at BCI- Blood And Cancer Institute, so that you are better informed and are able to take timely action.
Types of Lymphoma
There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
● Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL): This type is marked by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, a specific abnormal cell seen under a microscope. HL is relatively rare but often highly treatable, especially when diagnosed early. It commonly affects young adults and has high survival rates with appropriate therapy.
● Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL): This group includes a wide variety of lymphomas that do not have Reed-Sternberg cells. NHL is more common and can vary greatly in how fast it grows and spreads. Some types of NHL are aggressive and require immediate treatment, while others are indolent and may be monitored without immediate intervention.
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of lymphoma early can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment. Cancer specialist in Surat list its common signs:
● Swollen lymph nodes, often painless, in the neck, armpits, or groin
● Fever without an obvious infection
● Night sweats that soak clothing and sheets
● Unexplained weight loss
● Persistent fatigue and weakness
● Itchy skin that doesn’t go away
● Shortness of breath or chest pain, particularly if lymph nodes in the chest are affected
These symptoms can also result from less serious illnesses, but if they persist for more than a couple of weeks, it’s wise to consult a doctor.
Risk Factors
Hemato-oncologists in Surat lists certain factors that may increase the risk of developing lymphoma:
● Age: Some types are more common in young adults, while others occur more frequently in older adults.
● Gender: Males are slightly more likely to develop certain types of lymphoma.
● Family History: A family history of lymphoma can increase an individual’s risk.
● Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, autoimmune diseases, or medications that suppress the immune system raise the risk.
● Infections: Certain viral and bacterial infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Hepatitis C, and Helicobacter pylori, are linked to lymphoma.
● Chemical Exposure: Long-term exposure to certain chemicals like pesticides and solvents may increase risk.
Diagnosis
To diagnose lymphoma, doctors usually start with a physical exam, paying special attention to any swollen lymph nodes. They may then order imaging tests such as CT scans, PET scans, or MRIs to look for enlarged nodes or other signs of disease. A biopsy — removing a small sample of lymph node tissue — is essential to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of lymphoma. Blood tests can assess overall health and identify markers that suggest lymphoma. In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy is also performed.
Treatment Options
Lymphoma treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. Common leukemia treatment in Surat include:
● Chemotherapy: The use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
● Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation to kill cancer cells in specific areas.
● Immunotherapy: Treatments that help the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells, such as monoclonal antibodies.
● Targeted Therapy: Drugs designed to specifically target cancer cell mechanisms, such as proteins or genes driving cancer growth.
● Stem Cell Transplant: In severe cases, patients may need a transplant to restore healthy bone marrow after intensive chemotherapy.
Specialists at blood cancer hospitals in Surat often use a combination of these therapies to achieve the best results. In some low-grade NHL cases, “watchful waiting” is recommended, delaying treatment until the disease shows signs of progression.
Living with Lymphoma
Being diagnosed with lymphoma is life-changing, but many people live long, full lives after treatment. Managing lymphoma often includes:
● Regular follow-up appointments to monitor for recurrence
● Managing side effects from treatments like fatigue, infections, or fertility issues
● Emotional support through counseling, therapy, or support groups
● Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques
Survivorship care plans are often created for individuals in remission, providing guidelines for monitoring and maintaining health.
Prognosis
The outlook for lymphoma patients has improved dramatically over the past few decades. Many types of lymphoma respond well to treatment, especially when detected early. Five-year survival rates vary depending on the type and stage of lymphoma, but advancements in therapies and blood cancer treatments in Surat continue to push survival rates higher. For example, the five-year survival rate for Hodgkin lymphoma is about 89%, while many forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma also have strong survival outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Understanding lymphoma helps demystify a complex disease and highlights the importance of awareness. Persistent symptoms should never be ignored, and seeking medical advice early can make a significant difference. With early detection, proper treatment, and ongoing support, many people diagnosed with lymphoma are able to lead vibrant, fulfilling lives. Staying informed, advocating for oneself in healthcare settings, and building a strong support network are vital steps toward managing lymphoma effectively and maintaining a good quality of life.
